Cyp2e1 and NAFLD: A Scientific Exploration
This article delves into the critical association between Cyp2e1 and NAFLD, elucidating the pathophysiological interactions and impacts on liver health. Cyp2e1 is a member of the cytochrome P450 enzymes that has been linked to the development of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), a growing health concern due to increasing obesity rates worldwide.
Introduction to Liver Health
The human liver, a vital organ, plays numerous roles, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. It serves as a central hub for many metabolic processes, maintaining homeostasis and regulating various biochemical pathways essential for life. Among the myriad enzymes within the liver, the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) family is particularly significant for metabolic processes. These enzymes are pivotal in the metabolism of drugs, hormones, and other substances, affecting everything from drug efficacy to the detoxification of harmful compounds. One such member of this family, Cyp2e1, has recently gained scrutiny for its role in liver-related conditions, very notably Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).
Understanding Cyp2e1
Cyp2e1 is an enzyme integral to the oxidative metabolism of several endogenous and exogenous substances. Expressed predominantly in the liver, Cyp2e1 is involved in the metabolism of ethanol, certain drugs, and carcinogens. Its unique ability to metabolize small, xenobiotic compounds allows the liver to process a broad array of substances that enter the body. Importantly, its involvement extends to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can result in oxidative stress—a key factor implicated in the pathogenesis of various liver diseases, including NAFLD. This oxidative stress can initiate a cascade of inflammatory processes that may ultimately lead to cellular damage and fatty liver accumulation.
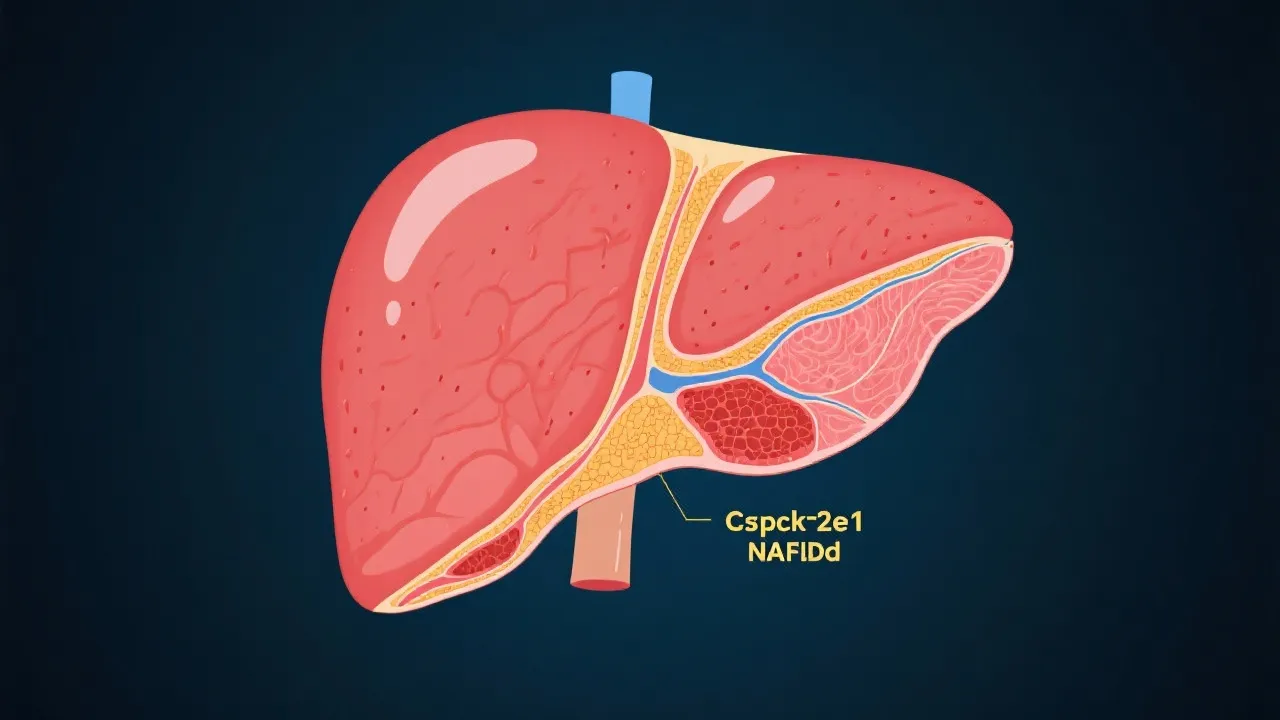
NAFLD: A Rising Concern
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver without significant alcohol consumption, is becoming increasingly prevalent in parallel with rising obesity rates globally. As lifestyle-related conditions rise, NAFLD has escalated into a leading cause of chronic liver disease, contributing to liver dysfunction and significant morbidity. Not only does NAFLD impair liver function, but it can also lead to more severe conditions, such as Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and ultimately cirrhosis, if left unchecked. The discovery of Cyp2e1’s involvement in these conditions underscores its relevance as a potential therapeutic target. This is particularly crucial in enhancing our understanding of how diet, metabolism, and specific enzymes interact in the progression of liver disease.
Mechanisms Linking Cyp2e1 to NAFLD
Cyp2e1 contributes to the liver’s oxidative stress by producing ROS. These highly reactive molecules can overwhelm the liver's antioxidant defenses, leading to a state of oxidative stress that has been shown to play a significant role in the progression of NAFLD. This oxidative stress can exacerbate lipid peroxidation, pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and mitochondrial dysfunction, which are all central to the pathogenesis of NAFLD. Research has demonstrated that increased expression and activity of Cyp2e1 have been observed in experimental models of NAFLD, implicating it directly in the disease's pathology. The chronic activation of Cyp2e1 not only promotes the accumulation of toxic metabolites but also contributes to cell signaling pathways that promote inflammation and fibrosis within the liver.
Comparative Analysis: General Liver Enzymes vs. Cyp2e1
| Enzyme | Role in Liver | Impact on NAFLD |
|---|---|---|
| Cyp2e1 | Metabolizes toxins and drugs; produces reactive oxygen species | Promotes oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to liver damage |
| Other CYP450 Enzymes | Varied roles in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids | Generally involved in metabolic processing; less specific to NAFLD |
| Cyp1a2 | Involved in the metabolism of caffeine and other substances | May contribute to drug interactions but less directly linked to NAFLD |
| Cyp3a4 | Responsible for metabolizing over half of all medications | Helps maintain overall hepatic function but not a direct contributor to NAFLD |
This comparative analysis illustrates that while many liver enzymes play essential roles in overall liver health, Cyp2e1’s specific functions make it particularly relevant in the discussion of NAFLD. Understanding these differences is crucial when considering treatment strategies that either target Cyp2e1 directly or enhance the liver’s capacity to compensate for its detrimental effects.
Implications for Treatment
The connection between Cyp2e1 and NAFLD paves the way for novel therapeutic strategies. Targeting the enzyme itself, or its downstream effects, could open avenues for interventions aimed at reducing hepatic oxidative stress, thereby mitigating NAFLD progression. Current research is exploring various options, including the use of antioxidants, Cyp2e1 inhibitors, and lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise. Antioxidants, which can neutralize ROS, are of particular interest as they may help restore the balance between oxidative stress and the liver’s antioxidant capacity. Clinical trials are underway to assess the efficacy of these agents in improving liver outcomes in patients with NAFLD.
Lifestyle Factors and Cyp2e1
While pharmacological approaches are critical, lifestyle modifications play an equally important role in managing NAFLD and influencing Cyp2e1 activity. Diet, physical activity, and weight management have well-documented effects on liver health. For instance, reducing caloric intake and increasing physical activity can lead to weight loss, thereby decreasing liver fat accumulation and potentially reducing Cyp2e1 expression. Research is increasingly suggesting that diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber may help ameliorate the effects of oxidative stress in the liver.
Furthermore, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption—despite NAFLD being a condition that occurs without significant alcohol intake—could also benefit liver health by reducing Cyp2e1 activity, given the enzyme’s role in ethanol metabolism. The relationship between diet, lifestyle choices, and Cyp2e1 function illustrates the complexity of NAFLD management and the necessity for a holistic approach to treatment.
Future Research Directions
The ongoing investigation into Cyp2e1’s role in NAFLD demands a multifaceted approach, integrating molecular biology, pharmacology, and clinical research. Future studies could further delineate the enzyme’s interactions with other metabolic pathways, and explore safe and effective inhibitors. For example, research into herbal compounds and natural products has yielded promising results, revealing potential inhibitors of Cyp2e1 that may offer fewer side effects than traditional pharmaceuticals. The ultimate aim is to develop interventions that can either prevent the progression of NAFLD or reverse its effects altogether.
Moreover, studies examining the genetic and epigenetic factors influencing Cyp2e1 expression could elucidate why some individuals are more susceptible to NAFLD than others. Such insights might pave the way for personalized treatment strategies based on an individual’s genetic makeup, allowing for more tailored and effective therapy. The incorporation of patient-specific data, including dietary habits, lifestyle, and genetic predisposition, will be critical in designing comprehensive treatment protocols for NAFLD.
FAQs
- What is Cyp2e1?
Cyp2e1 is an enzyme from the cytochrome P450 family involved in the metabolism of various substances, including drugs and toxins, and is notable for producing reactive oxygen species. - Why is NAFLD a public health concern?
NAFLD is increasingly common due to lifestyle factors and can lead to severe liver damage, including cirrhosis, if not managed properly. Its prevalence correlates closely with rising rates of obesity and metabolic syndrome. - How is Cyp2e1 linked to oxidative stress?
Cyp2e1 contributes to oxidative stress through the generation of reactive oxygen species, which can damage liver cells and contribute to NAFLD progression. This oxidative stress is a key player in the inflammatory processes associated with fatty liver disease. - Are there treatments targeting Cyp2e1?
Current research focuses on antioxidants and potential Cyp2e1 inhibitors as strategies to reduce hepatic oxidative stress in NAFLD. It is essential to explore both pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches.
By understanding the pivotal role Cyp2e1 plays in the liver’s function and pathology, healthcare professionals and researchers can better address the challenges presented by NAFLD. The ongoing efforts to unravel the complexities of Cyp2e1 can offer fresh perspectives and hope for more effective treatments in the future. The integration of lifestyle interventions, pharmacological advances, and ongoing research into individual genetic factors could lead to a comprehensive approach to manage and potentially reverse NAFLD effectively.