Understanding Seimc Hepatitis Implications
Seimc Hepatitis is a significant subtype of liver inflammation involving unique characteristics that set it apart from other types. It requires careful management due to its potential severity. In understanding this condition, it is crucial to consider its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment approaches, along with exploring ongoing research and expert insights into its future management and prevention.
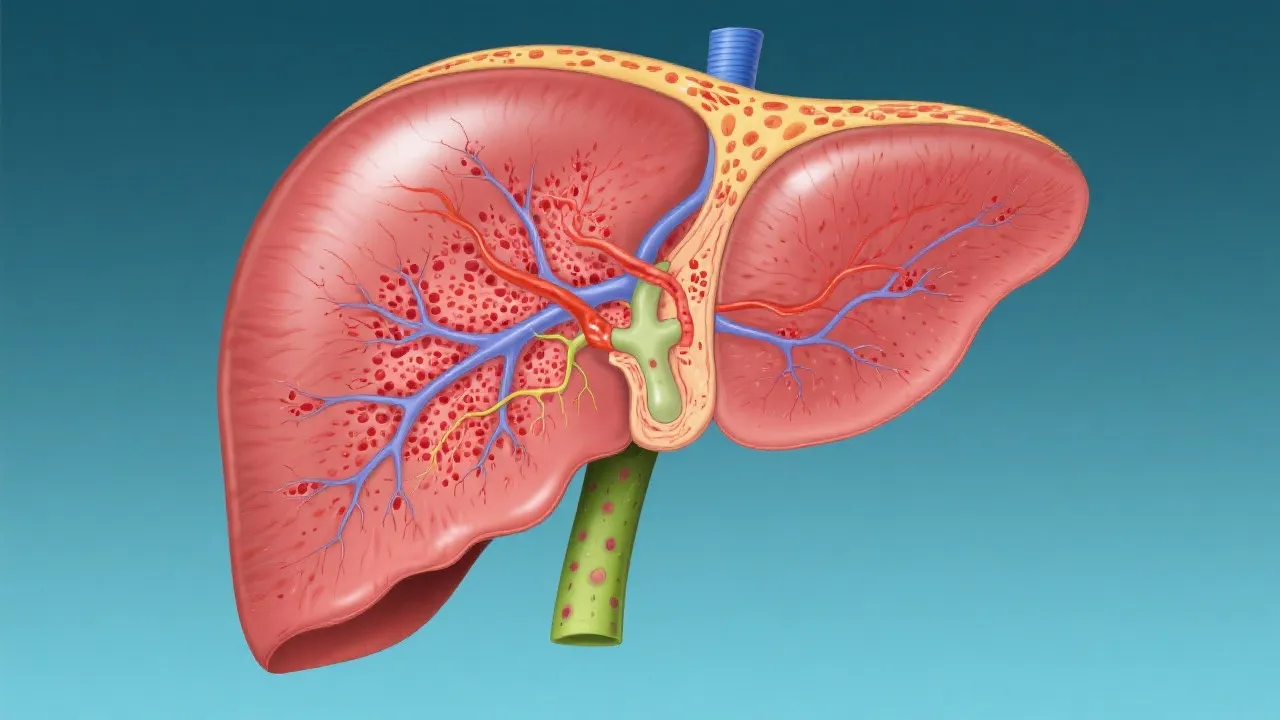
Introduction to Seimc Hepatitis
Seimc Hepatitis represents a particular subtype of hepatitis, distinguished by its specific etiological and pathological characteristics. Unlike more mainstream forms of hepatitis that are viral in nature, Seimc Hepatitis requires an in-depth understanding of its unique causative factors and progression. This article aims to delve into the facets of Seimc Hepatitis by exploring its presentation, diagnostic approaches, and current research aimed at improving patient outcomes.
Understanding Hepatitis
Hepatitis, in general, refers to the inflammation of the liver and can arise from various causes, including viral infections, autoimmune responses, toxic substances, and heavy alcohol use. Each type of hepatitis presents its challenges, requiring tailored approaches in diagnosis and management. The liver is essential for metabolism and detoxification; when inflamed due to hepatitis, it can lead to significant health issues, including liver cirrhosis and carcinoma. Hepatitis can affect individuals differently, depending on factors like age, sex, genetic predisposition, and overall health. Understanding these differences is vital for effective treatment and management strategies for each subtype.
Etiology and Pathophysiology of Seimc Hepatitis
The underlying causes of Seimc Hepatitis are not as well understood compared to viral hepatitis forms such as Hepatitis A, B, and C. Current research suggests that it may involve atypical immune responses, environmental toxins, or even genetic factors. While the exact etiological factors may remain elusive, studies have indicated potential associations with certain drugs, dietary elements, and other lifestyle choices that could trigger the disease.
The pathophysiology of Seimc Hepatitis involves complex interactions between the immune system and liver cells, resulting in inflammation and hepatocyte damage. The immune response may result in either a direct attack on liver cells or an exaggerated inflammatory response that causes collateral damage. This distinction is crucial, as therapies may focus on modulating the immune response or addressing the underlying triggers to prevent further liver damage.
Furthermore, inflammation can lead to a cascade effect within the liver, initiating fibrosis. If not managed appropriately, this process can evolve to severe complications such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, thereby underscoring the importance of early diagnosis and intervention in managing Seimc Hepatitis.
Diagnostic Approach
Diagnosing Seimc Hepatitis involves a multifaceted approach, including a patient's clinical history, biochemical tests, and advanced imaging techniques. Liver function tests are pivotal in revealing inflammation levels, while imaging assists in structural assessments. Blood tests can indicate elevated liver enzymes, which suggest inflammation or damage to hepatocytes. Additionally, more specific tests aimed at identifying potential autoimmune markers may aid in the consideration of Seimc Hepatitis as a diagnosis.
In some cases, a liver biopsy may be warranted to provide a definitive diagnosis through histological examination. This step can give insight into the extent of liver damage and inflammation, guiding treatment strategies. Advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, can visualize liver architecture and identify abnormalities or complications that may accompany Seimc Hepatitis.
Emerging techniques in diagnostic imaging, like elastography, which measures liver stiffness as an indicator of fibrosis, are becoming integral tools in the assessment of chronic liver disease, including Seimc Hepatitis. Incorporating these advanced methods enhances diagnostic accuracy and facilitates timely management decisions.
Treatment Modalities
Treatment of Seimc Hepatitis focuses on managing symptoms and mitigating liver damage. While no specific antiviral treatment exists as with other forms of viral hepatitis, a comprehensive approach combining medications, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring of liver function is crucial. Depending on the severity of the condition, healthcare providers may recommend corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive drugs to address inflammation and immune-mediated liver damage.
Lifestyle changes, such as dietary adjustments, minimizing environmental toxin exposure, and alcohol abstinence, play a crucial role in managing Seimc Hepatitis. A liver-friendly diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while avoiding high-fat, sugary, and processed foods, can support liver health. Regular exercise also contributes to maintaining a healthy weight, which can alleviate stress on the liver.
Regular follow-ups are essential, as they help in monitoring liver function over time. This management approach not only aims to address immediate symptoms but also to prevent long-term complications such as cirrhosis or liver failure. Depending on individual needs, referral to specialists such as hepatologists or dietitians can further enhance treatment effectiveness.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
As our understanding of Seimc Hepatitis’s etiology and progression improves, ongoing research into novel therapies offers hope for more effective management. Studies are currently investigating the genetic markers associated with predisposition to the condition, which could lead to personalized medicine approaches in treatment. Targeted therapies that address specific pathways involved in its pathogenesis are also in development, paving the way for more precise interventions that may significantly improve patient outcomes.
Current clinical trials exploring various modalities—from new immunotherapy approaches to innovative drug compounds—are critical in redefining the management landscape of Seimc Hepatitis. Evidence-based strategies are emerging to address the multifactorial nature of the disease, which could lead to breakthroughs in treatment protocols. The promise of gene therapy and advancements in nanotechnology could further revolutionize how Seimc Hepatitis is treated in the near future.
Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patients will be essential to translating laboratory findings into practical treatment strategies. Increasing awareness and understanding of Seimc Hepatitis among the medical community and the general public remain crucial for early detection and intervention strategies.
Impact of Seimc Hepatitis on Patients' Quality of Life
The impact of Seimc Hepatitis extends beyond the biochemical markers and clinical symptoms; it significantly affects the quality of life of those diagnosed with the condition. Patients often experience a range of emotions, from fear and frustration to anxiety about the future, especially if their diagnosis is unclear or evolving. The uncertainty surrounding the condition can lead to stress, which itself may exacerbate physical symptoms.
Moreover, the chronic nature of liver diseases often necessitates lifestyle alterations that may feel restrictive. Dietary changes, increased healthcare appointments, and potential modifications to work and social activities can strain personal relationships and affect mental well-being. Therefore, addressing these psychosocial aspects becomes as important as the clinical management of Seimc Hepatitis.
Support systems, including family involvement and patient support groups, can play a transformative role in helping individuals navigate their diagnosis. Emotional support, alongside professional counseling when necessary, can significantly mitigate feelings of isolation or helplessness that patients may experience. Healthcare providers should routinely inquire about psychosocial feelings so they can provide holistic support that addresses both physical and emotional needs.
Comparison Table of Hepatitis Subtypes
| Type | Cause | Primary Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Viral Hepatitis A | Hepatitis A virus | Fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice |
| Viral Hepatitis B | Hepatitis B virus | Joint pain, dark urine, fever |
| Seimc Hepatitis | Unknown complex factors | Varied; can be asymptomatic initially |
Role of Lifestyle and Prevention
Prevention remains a cornerstone in managing any type of hepatitis. For Seimc Hepatitis, this can involve minimizing exposure to known environmental toxins and adopting a liver-friendly lifestyle. Regular health check-ups and early detection strategies are advisable for at-risk individuals, ensuring timely intervention. This preventive approach also emphasizes public health measures and education to raise awareness among populations that may be more vulnerable due to environmental, occupational, or genetic factors.
Individuals can also benefit from understanding their family medical history, as such knowledge can illuminate potential risks for liver disease, including Seimc Hepatitis. By forging connections between personal history and health decisions, early strategic intervention becomes feasible.
Adopting practices such as stress management techniques, regular physical activity, and adequate hydration can bolster liver health and reduce the risk of developing Seimc Hepatitis or exacerbating existing liver conditions. Engaging in regular medical consultations allows healthcare providers to assist in cultivating supportive environments that can enhance liver health.
FAQs
- What are the main symptoms of Seimc Hepatitis? Initially, symptoms may be mild or absent; however, as the condition progresses, fatigue, jaundice, and abdominal discomfort may develop. Patients may also report non-specific symptoms such as weight loss or decreased appetite.
- Is Seimc Hepatitis contagious? Unlike viral forms, Seimc Hepatitis is not typically contagious, but its exact mode of transmission is still under study. Understanding possible environmental triggers can further elucidate potential risk factors for individuals.
- How can Seimc Hepatitis be managed effectively? Management involves medical intervention, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals to adapt treatment strategies based on individual responses and progression of the disease.
Conclusion
Seimc Hepatitis poses various challenges and requires a concerted effort from both healthcare professionals and patients to mitigate its impacts on liver health. Continuous research and advancements in medical science are pivotal in understanding this complex condition better and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. Integrating comprehensive care strategies that embrace both medical and psychosocial aspects will empower those impacted by Seimc Hepatitis, supporting them in leading fulfilling lives despite their diagnosis.